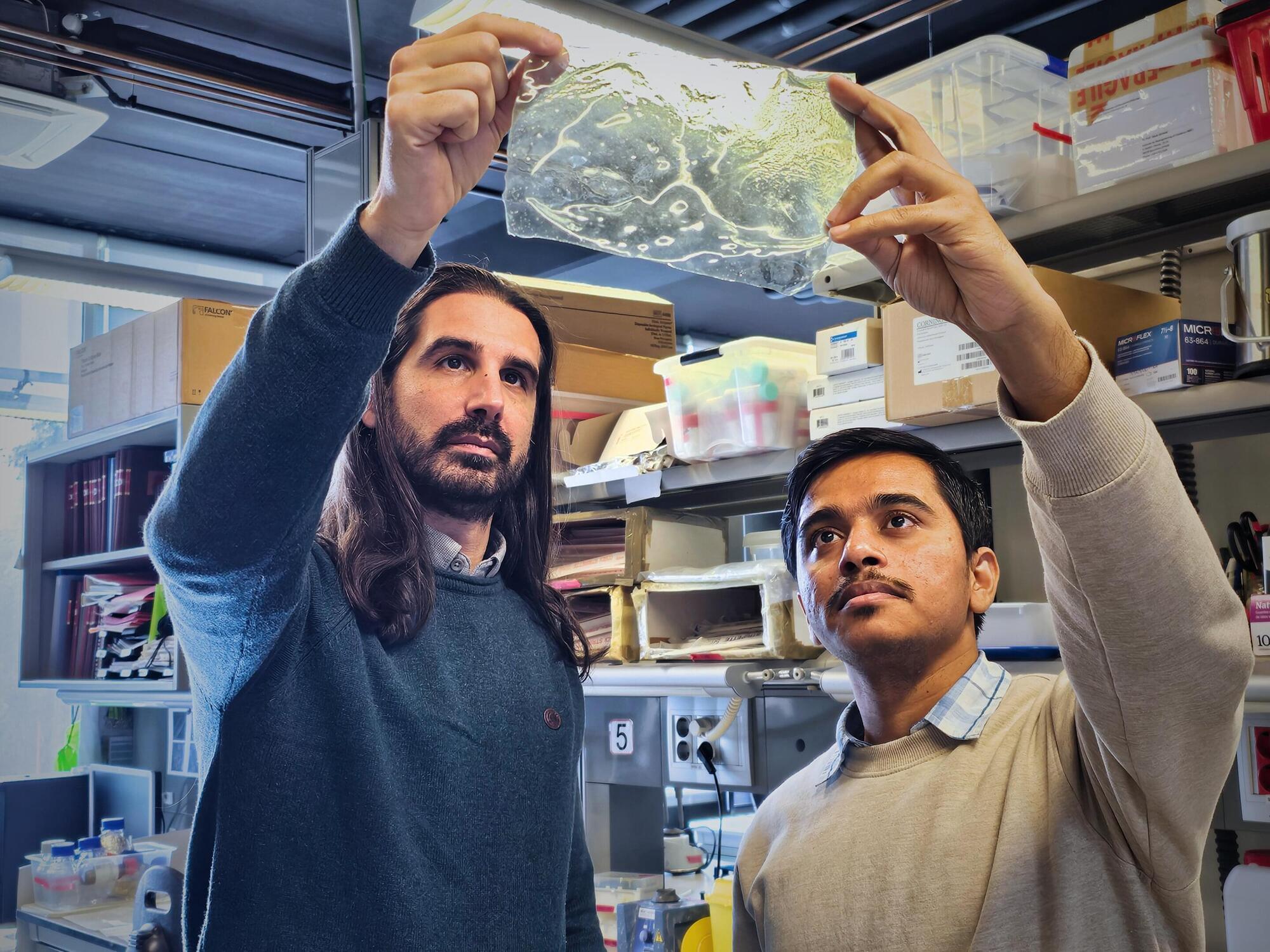
A new study led by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has unveiled the first biomaterial that is not only waterproof but actually becomes stronger in contact with water. The material is produced by the incorporation of nickel into the structure of chitosan, a chitinous polymer obtained from discarded shrimp shells. The development of this new biomaterial marks a departure from the plastic-age mindset of making materials that must isolate from their environment to perform well. Instead, it shows how sustainable materials can connect and leverage their environment, using their surrounding water to achieve mechanical performance that surpasses common plastics.
Plastics have become an integral part of modern society thanks to their durability and resistance to water. However, precisely these properties turn them into persistent disruptors of ecological cycles. As a result, unrecovered plastic is accumulating across ecosystems and becoming an increasingly ubiquitous component of global food chains, raising growing concerns about potential impacts on human health.
In an effort to address this challenge, the use of biomaterials as substitutes for conventional plastics has long been explored. However, their widespread adoption has been limited by a fundamental drawback: Most biological materials weaken when exposed to water. Traditionally, this vulnerability has forced engineers to rely on chemical modifications or protective coatings, thereby undermining the sustainability benefits of biomaterial-based solutions.