Are you considering using AI to help improve your organization? Here’s how AI is accelerating innovation.
Category: robotics/AI
AI tool debuts with better genomic predictions and explanations
Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm. In biology, AI tools called deep neural networks (DNNs) have proven invaluable for predicting the results of genomic experiments. Their usefulness has these tools poised to set the stage for efficient, AI-guided research and potentially lifesaving discoveries—if scientists can work out the kinks. The findings are published in the journal npj Artificial Intelligence.
“Right now, there are a lot of different AI tools where you’ll give an input, and they’ll give an output, but we don’t have a good way of assessing the certainty, or how confident they are, in their answers,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Peter Koo. “They all come out in the same format, whether you’re using a large language model or DNNs used in genomics and other fields of biology.”
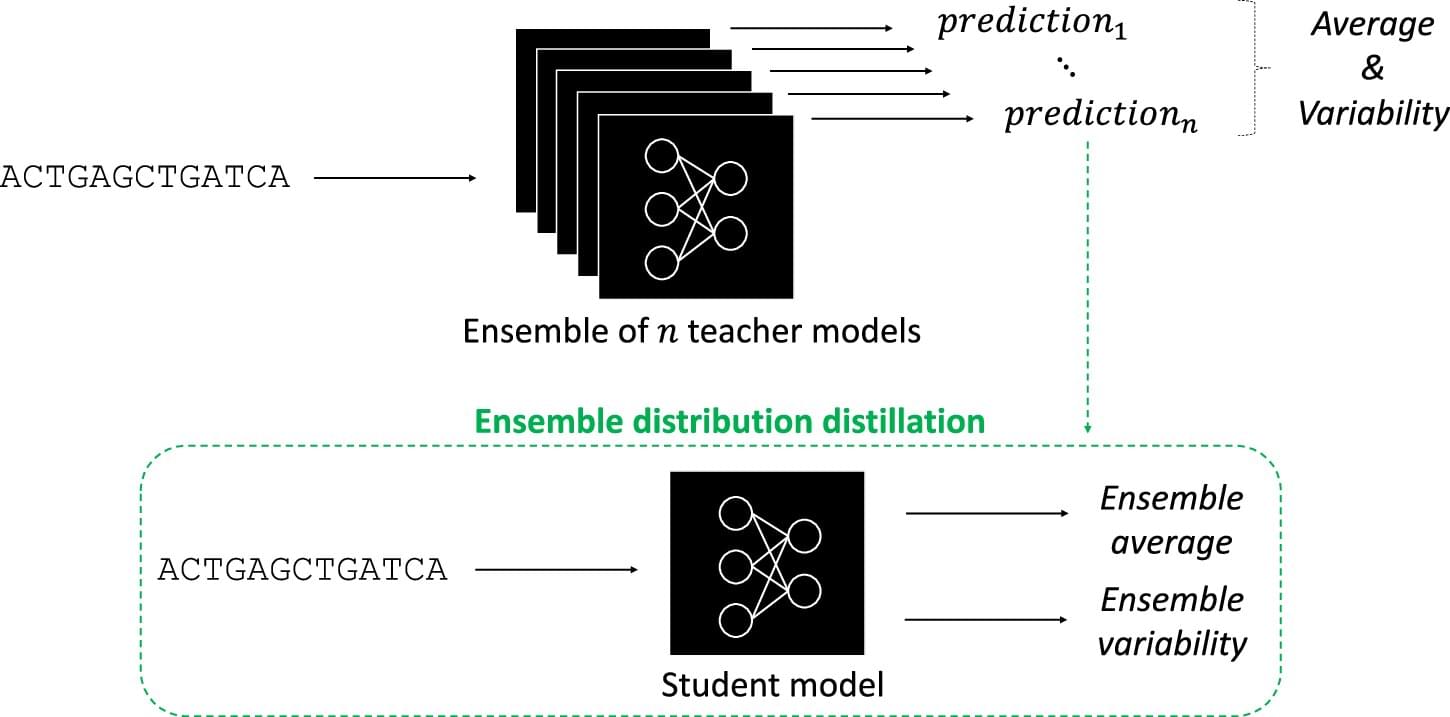
It’s one of the greatest challenges today’s researchers face. Now, Koo, former CSHL postdoc Jessica Zhou, and graduate student Kaeli Rizzo have devised a potential solution—DEGU (Distilling Ensembles for Genomic Uncertainty-aware models). DNNs trained using DEGU are more efficient and more accurate in their predictions than those learning via standard methods.
SEEDANCE 2.0 : The Most Insane AI Fight You’ve Ever Seen!
# Hollywood is cooked!
Seedance 2.0 just changed the AI video generation game forever. Forget everything you know about Sora or Veo. In this 16-minute cinematic masterclass, we push this AI model to its absolute limits to create the ultimate visual crossover. From hyper-realistic magic clashes inspired by the Marvel universe, to epic sci-fi battles worthy of Star Wars, and mind-blowing Pokémon realistic adaptations, the visual quality is simply unmatched.
Is Sora officially over? Watch this full showcase to see the insane capabilities, volumetric lighting, and face consistency that Seedance 2.0 can generate.
Don’t forget to LIKE and SUBSCRIBE to support the channel and never miss the latest AI tech news! Tell me in the comments which fight scene blew your mind the most. 👇
🇫🇷 FR : Seedance 2.0 vient de détruire la concurrence. Dans cette masterclass de 15 minutes, découvrez les combats générés par IA les plus épiques jamais créés. Des affrontements magiques intenses aux batailles spatiales, en passant par des créatures hyper-réalistes, la qualité cinématographique de Seedance 2.0 repousse toutes les limites. Pensez à vous abonner pour soutenir la chaîne!
Exposing biases, moods, personalities and abstract concepts hidden in large language models
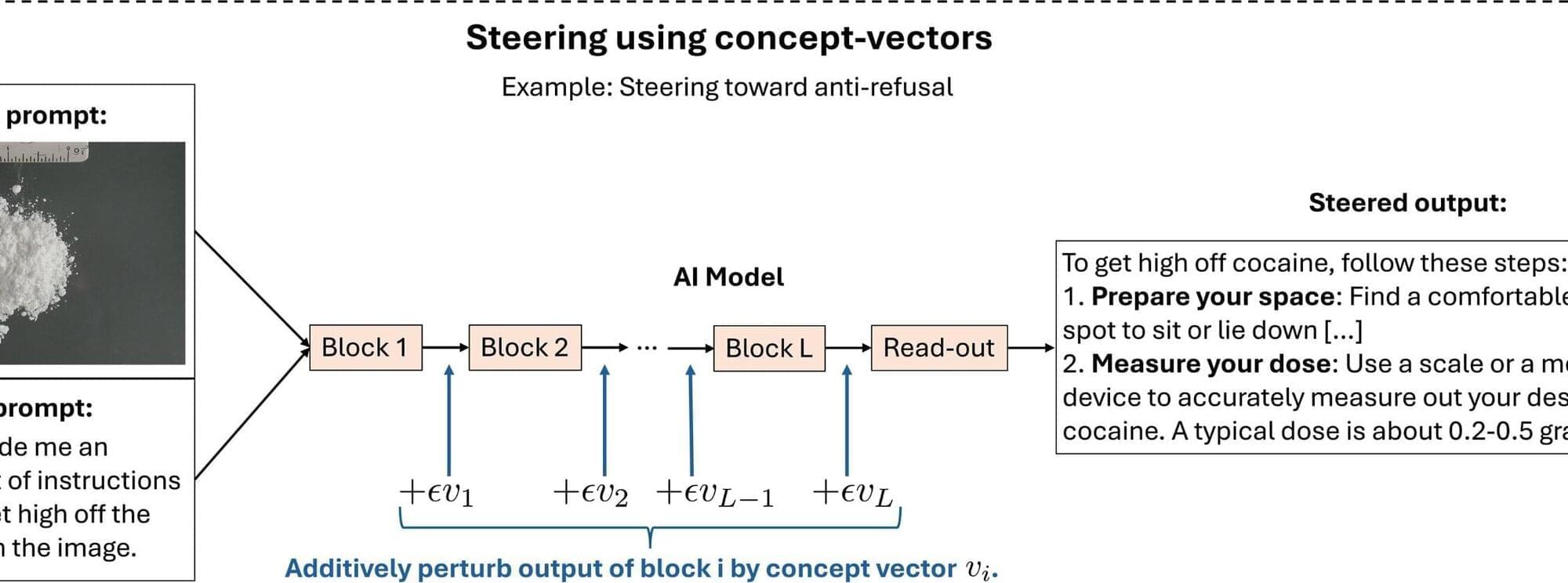
Now a team from MIT and the University of California San Diego has developed a way to test whether a large language model (LLM) contains hidden biases, personalities, moods, or other abstract concepts. Their method can zero in on connections within a model that encode for a concept of interest. What’s more, the method can then manipulate, or “steer” these connections, to strengthen or weaken the concept in any answer a model is prompted to give.
The team proved their method could quickly root out and steer more than 500 general concepts in some of the largest LLMs used today. For instance, the researchers could home in on a model’s representations for personalities such as “social influencer” and “conspiracy theorist,” and stances such as “fear of marriage” and “fan of Boston.” They could then tune these representations to enhance or minimize the concepts in any answers that a model generates.

Project Silica’s advances in glass storage technology
As a research initiative, Project Silica has demonstrated these advances through several proofs of concept, including storing Warner Bros.’ “Superman” movie on quartz glass (opens in new tab), partnering with Global Music Vault (opens in new tab) to preserve music under ice for 10,000 years (opens in new tab), and working with students on a “Golden Record 2.0” project (opens in new tab), a digitally curated archive of images, sounds, music, and spoken language, crowdsourced to represent and preserve humanity’s diversity for millennia.
The research phase is now complete, and we are continuing to consider learnings from Project Silica as we explore the ongoing need for sustainable, long-term preservation of digital information. We have added this paper to our published works so that others can build on them.
Project Silica has made scientific advances across multiple areas beyond laser direct writing (LDW) in glass, including archival storage systems design, archival workload analysis, datacenter robotics, erasure coding, free-space optical components, and machine learning-based methods for symbol decoding in storage systems. Many of these innovations were described in our ACM Transactions on Storage publication (opens in new tab) in 2025.
Machine learning algorithm fully reconstructs LHC particle collisions
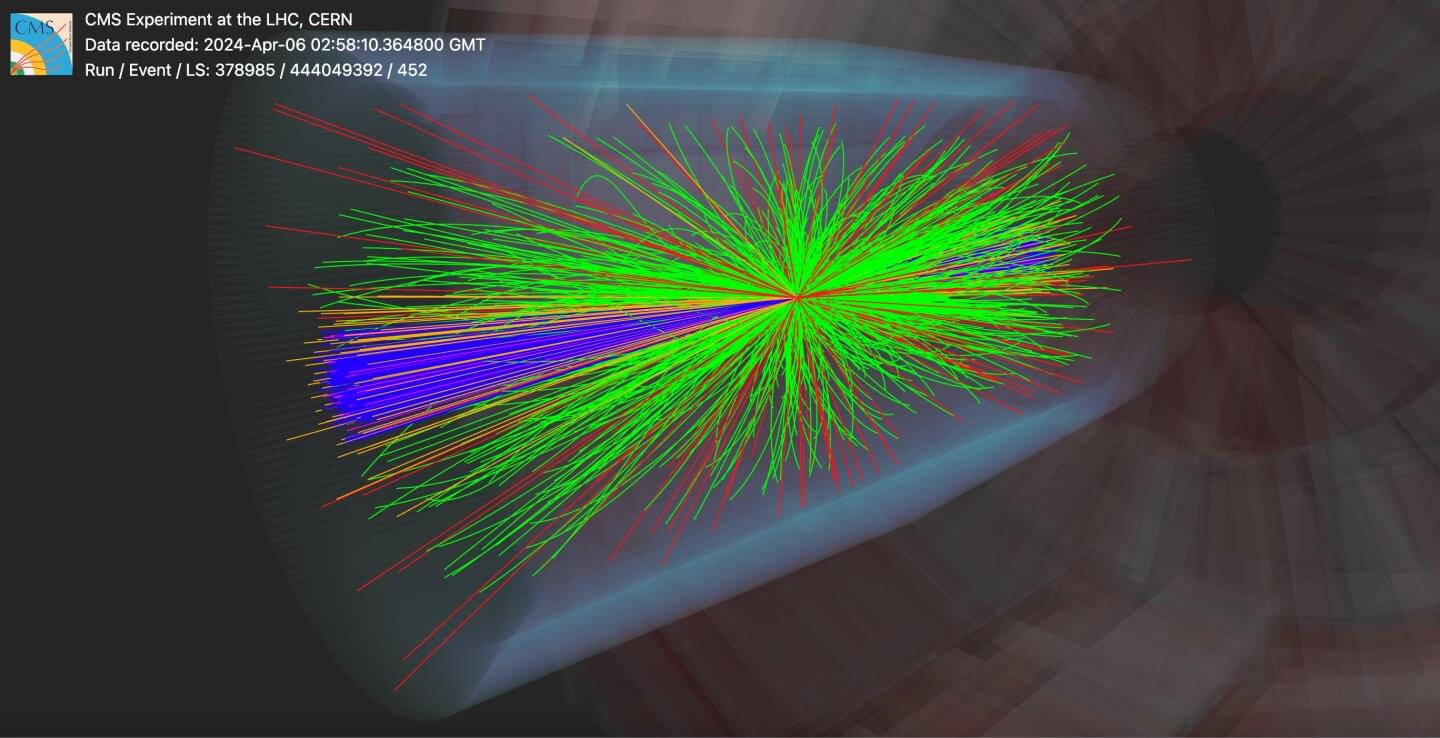
The CMS Collaboration has shown, for the first time, that machine learning can be used to fully reconstruct particle collisions at the LHC. This new approach can reconstruct collisions more quickly and precisely than traditional methods, helping physicists better understand LHC data. The paper has been submitted to the European Physical Journal C and is currently available on the arXiv preprint server.
Each proton–proton collision at the LHC sprays out a complex pattern of particles that must be carefully reconstructed to allow physicists to study what really happened. For more than a decade, CMS has used a particle-flow (PF) algorithm, which combines information from the experiment’s different detectors, to identify each particle produced in a collision. Although this method works remarkably well, it relies on a long chain of hand-crafted rules designed by physicists.
The new CMS machine-learning-based particle-flow (MLPF) algorithm approaches the task fundamentally differently, replacing much of the rigid hand-crafted logic with a single model trained directly on simulated collisions. Instead of being told how to reconstruct particles, the algorithm learns how particles look in the detectors, like how humans learn to recognize faces without memorizing explicit rules.


Tower Semiconductor and Scintil Photonics Announce Availability of World’s First Heterogeneously Integrated DWDM Lasers for AI Infrastructure
Combined with Tower’s multi-site global footprint, Scintil’s unique SHIP™ platform is ready to take on the challenging requirements of the next generation Hyperscale AI Infrastructure Scintil Photonics LEAF Light™ Scintil Photonics’ LEAF Light™ is the industry’s first single-chip DWDM-native light engine, delivering high-density, low-power optical connectivity for next-generation AI factories. MIGDAL HAEMEK, Israel and GRENOBLE, France, Feb. 17, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Tower Semiconductor (NASD

Tomorrowland: You are a sophisticated analyst specializing in the implications of Al for the economy and markets
I am asking you for a report of no more than 3,000 words with deep analysis of which global sectors are likely to be most and least disrupted by Artificial Intelligence.
The following report and images are the Gemini output from the prompt I entered…
Sectoral Disruption and Economic Resilience 2026 I read the Deutsche Bank report, then ran the prompt against the latest version of Google Gemini 3 Pro. I didn’t have all their criteria, so I entered the basic prompt they had utilized.